APLS: Average Path Length Similarity
Contents
- 1. Introduction to APLS
- 2. Road Network as a Graph
- 3. Challenges in Evaluating Road Network Extraction Models
- 4. APLS – A New Metric for Road Network Evaluation
- 5. Node Snapping Procedure in APLS
- 6. References
1. Introduction to APLS
APLS (Average Path Length Similarity) is a recently developed metric designed to evaluate the performance of road network extraction models, especially in the SpaceNet3 challenge. SpaceNet3 is a prominent benchmark in satellite image processing for extracting road maps using large and diverse datasets.
2. Road Network as a Graph
A road network can be represented as a graph, where nodes correspond to intersections or key points on roads, and edges represent road segments connecting these nodes. This representation enables solving problems like shortest path computation, connectivity analysis, and traffic simulation.
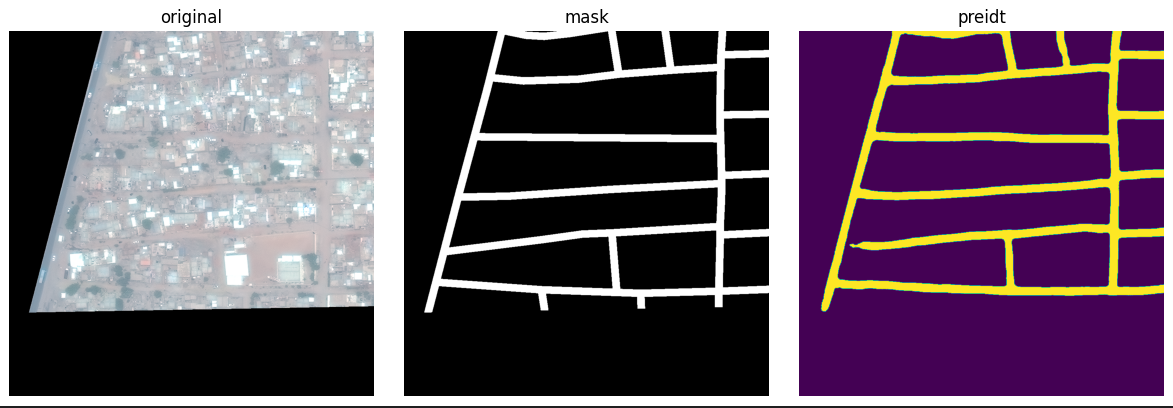 The deep learning model tries to "segment" road pixels from the image and convert them into a road graph
The deep learning model tries to "segment" road pixels from the image and convert them into a road graph
Ground Truth Road Network Graph
Illustration of shortest path finding using Dijkstra’s algorithm (compared with real data on Google Earth – view here)
3. Challenges in Evaluating Road Network Extraction Models
Traditional evaluation metrics for road network extraction often rely on pixel-based measures like IoU or pixel accuracy. However, these metrics do not fully capture the quality of the network’s structure, such as connectivity or accuracy of road segments.
This limitation makes it difficult to accurately assess a model’s ability to generate practically useful road maps.
4. APLS – A New Metric for Road Network Evaluation
APLS was designed to address the shortcomings of traditional pixel-based metrics by comparing shortest paths in the true network and the predicted network. It measures the similarity in structure and path lengths between the two graphs to more accurately evaluate road extraction quality.
APLS Path Score Formula (C):
\[C = 1 - \frac{1}{N} \sum \min\left\{1, \frac{\left|L(a,b) - L(a', b')\right|}{L(a,b)}\right\}\]Where:
- ( N ): The number of unique paths.
- ( L(a,b) ): The shortest path length between nodes (a) and (b) in the ground truth graph.
- ( L(a’, b’) ): The shortest path length between the corresponding nodes (a’) and (b’) in the predicted graph.
- The sum is taken over all source (a) and target (b) node pairs in the ground truth graph.
- ( a’, b’ ): Nodes in the predicted graph corresponding to (a, b) after snapping.
The value of (C) ranges from 0 (poor) to 1 (perfect), indicating how closely the predicted graph matches the ground truth in terms of path structure.
Remarks:
- APLS emphasizes evaluating network structure, especially important road segments with high usage frequency (related to betweenness centrality), helping detect major errors like missing segments or disconnected paths.
- If the shortest path between two nodes does not exist in the predicted graph (i.e., missing road segments), a maximum penalty of 1.0 is applied, causing a significant drop in the APLS score.
- This ensures that missing or disconnected roads are heavily penalized, emphasizing the need for correctly connected road networks in predictions.
- The calculation involves two snapping steps, one from ground truth to prediction and one vice versa, enabling a comprehensive evaluation that captures errors on both sides.
- Therefore, APLS is considered an effective and appropriate metric for evaluating road network extraction from satellite imagery or complex geographic data.
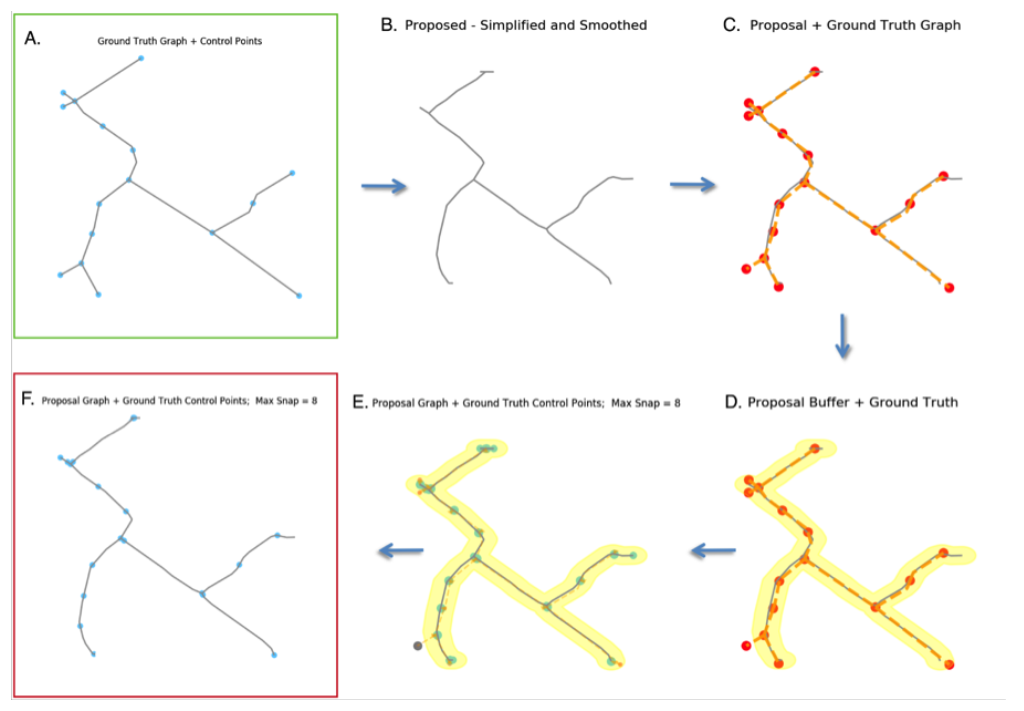
5. Node Snapping Procedure in APLS
B: Proposed graph.
C: Ground truth graph (orange) and control nodes (red) overlaid on the proposed graph (gray).
D: As in C, with an added buffer area (yellow) around the proposed graph.
E: Control nodes of the ground truth graph snapped to the nearest edges of the proposed graph, except nodes outside the buffer (gray).
F: Final proposed graph with snapped nodes ready for comparison with graph A.
6. How APLS Works and References
[1] SpaceNet3 Road Detection and Routing Challenge. 🔗 https://spacenet.ai/spacenet-challenge/overview/
[2] Road Network Extraction and Evaluation using APLS. 🔗 https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.03563